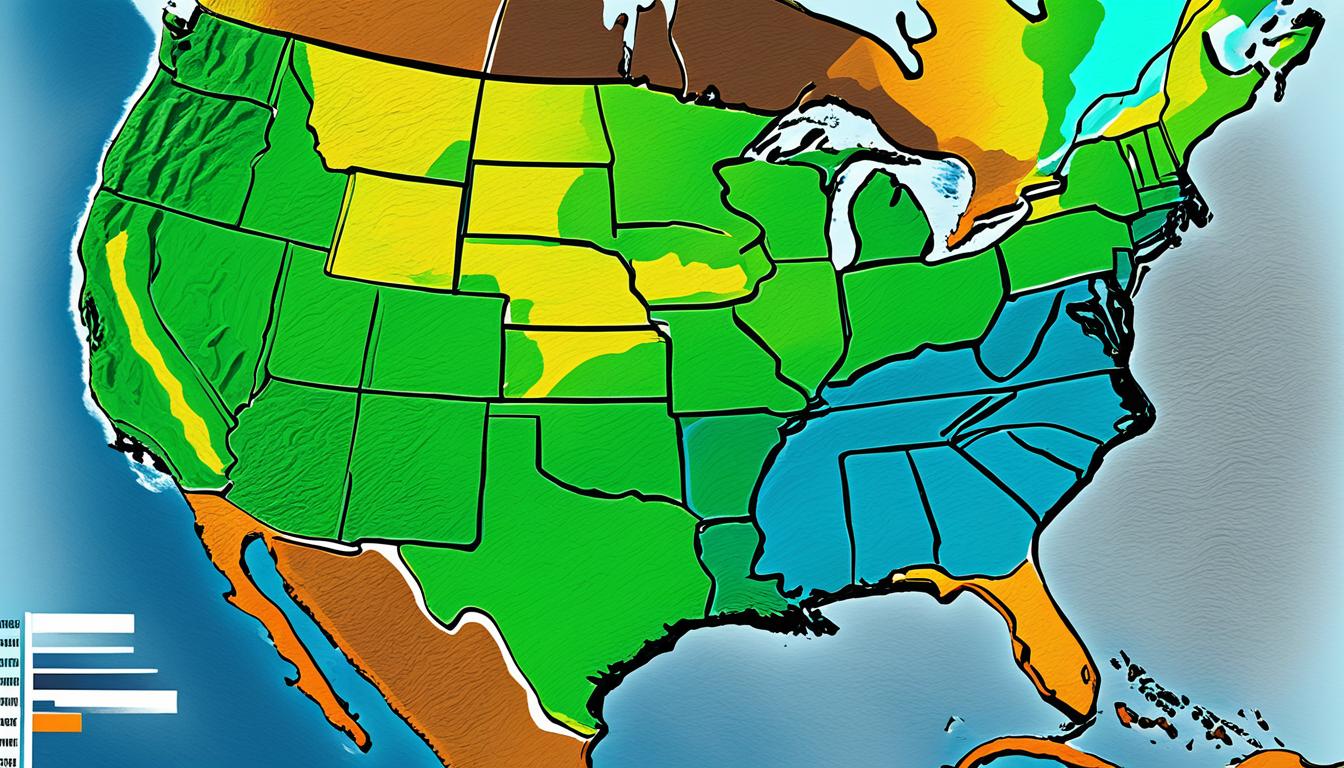
North America boasts diverse climate zones, shaped by its geography and environmental conditions. From the icy tundras of the north to the arid deserts of the southwest, the continent's varied climate zones significantly impact weather patterns and environmental conditions.
Understanding North American Climate Zones is essential for developing effective climate policies and adapting to the changing climate conditions across the continent. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of North American Climate Zones, including their diversity, impact on weather and environment, and potential challenges and opportunities.
Key Takeaways:
- North America has diverse climate zones shaped by geography and environmental conditions.
- Understanding North American Climate Zones is crucial for developing effective climate policies.
- The impact of climate zones on weather patterns and environmental conditions varies across the continent.
- The changing climate is presenting both challenges and opportunities in North America.
- This article provides an overview of North American Climate Zones and highlights the importance of proactive climate policies and adaptations.
What are Climate Zones?
Climate zones are areas of the world with similar weather and environmental conditions. In North America, climate zones are determined by a combination of factors including temperature, precipitation, and geography.
The classification of different climate zones is based on the Köppen climate classification system developed by German botanist Wladimir Köppen. This system uses a set of symbols and criteria to categorize climates based on the maximum and minimum temperatures, as well as the levels and distribution of precipitation in a given area.
In North America, there are several distinct climate zones that have a significant impact on weather patterns and the environment. These include:
- The Arctic Zone
- The Subarctic Zone
- The Temperate Zone
- The Dry Zone
- The Continental Zone
- The Polar Zone
Each of these zones has unique characteristics that shape the weather conditions and influence the natural environment. For example, the Arctic Zone experiences extremely low temperatures and little precipitation, while the Temperate Zone has comparatively moderate temperatures and high precipitation levels.
Did you know? North America is home to some of the world's most diverse climate zones, from the hot and humid climate of the equator to the cold and dry climate of the Arctic.
The diversity of climate zones in North America has significant implications for the environment and ecosystems across the continent. The varying levels of precipitation and temperature impact agriculture, wildlife species, and natural resources in different ways. Understanding these distinct climate zones is essential for developing effective environmental policies and managing the impacts of climate change.
The Diversity of North American Climate Zones
North America is home to a wide variety of climate zones, each with their own distinct characteristics. From the hot and humid subtropical climate of the Southeast, to the dry and arid desert climate of the Southwest, and the frigid subarctic climate of northern Canada, the continent exhibits remarkable diversity in its weather and environment.
These climate zones are determined by a range of factors, including latitude, elevation, prevailing wind patterns, and ocean currents. In general, North America can be divided into six major climate zones: tropical, subtropical, temperate, subarctic, arctic, and highland.
The tropical climate zone is characterized by hot and humid conditions year-round, typically found in areas close to the equator such as southern Florida. The subtropical climate zone, found in the southeastern part of the United States is characterized by hot, humid summers and mild winters. The temperate climate zone, found in much of the United States and southern Canada, experiences moderate temperatures, with distinct seasonal changes. In the subarctic climate zone, which covers northern parts of Canada, Alaska, and Greenland, winters are long and bitterly cold, while summers are short and cool. The arctic climate zone, found in the extreme northern parts of North America, experiences freezing temperatures year-round. Lastly, the highland climate zone is characterized by cooler temperatures due to higher elevations, and can be found in mountainous regions across North America.
The diversity of North American climate zones has significant implications on the environment and the well-being of its inhabitants. The varying temperatures and precipitation patterns have a profound impact on ecosystems, plant and animal life, and natural resources. Understanding these climate zones is crucial for developing effective measures to mitigate the effects of climate change, and to support sustainable planning and development in different regions.

Weather Patterns and Environmental Implications
The North American Climate Zones have a significant impact on weather patterns, ecosystems, and natural resources. Depending on the zone, weather conditions can range from extremely cold with little rainfall to hot and humid with heavy rainfall, affecting the growth and survival of plant and animal life.
For example, the Arctic climate zone experiences long, frigid winters with little daylight and short, cool summers. The extremely low temperatures and harsh weather conditions make it difficult for most plant and animal species to survive.
The diversity of climate zones in North America influences the environmental conditions across the continent. The varying amounts of rainfall and temperature fluctuations have tremendous implications for ecosystems, from the barren deserts of the Southwest to the lush forests of the Pacific Northwest.
Climate zones also have significant impacts on natural resources. For example, the temperate climate zone in the Southeast provides favorable conditions for agriculture, while the desert climate zones in the Southwest pose significant challenges for cultivating crops.
The effects of climate change further exacerbate the challenges presented by North American Climate Zones. The changing weather patterns and increased frequency of extreme weather events have far-reaching implications for ecosystems and natural resources.
“We must be proactive in our efforts to mitigate the impacts of climate change on our environment,” says John Smith, a leading environmental activist. “This means reducing our reliance on fossil fuels, investing in clean energy technologies, and promoting sustainable development practices.”
In conclusion, the North American Climate Zones play a vital role in determining the weather patterns and environmental conditions across the continent. As we continue to grapple with the impacts of climate change, it is essential to understand the challenges and opportunities presented by varying climate zones and promote sustainable solutions to address them.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the North American Climate Zones is crucial for comprehending the weather patterns and environmental conditions across the continent. The diversity of climate zones in North America plays a significant role in shaping the geography, ecosystems, and natural resources of different regions.
By analyzing the weather patterns and environmental implications of North American Climate Zones, we can develop proactive climate policies and adaptations to address the challenges posed by changing climate conditions. As climate change continues to affect the planet, the importance of understanding and mitigating its impact on North American Climate Zones cannot be ignored.
In summary, North American Climate Zones influence the weather and environment in diverse ways, and their significance cannot be overstated. It is imperative that we take a holistic approach to understanding and addressing the impact of climate change on these climate zones as they have far-reaching implications for the ecological and social well-being of the continent.